ZVI 101: What is ZVI Remediation Emplacement and How Does It Work?
By: Deborah Shaffer Schnell, PEZero Valent Iron (ZVI) technology has been a preferred remediation tool for nearly 30 years. It's important for every environmental consultant to understand what ZVI is and how it works. For a deeper dive into ZVI emplacement, including suitable geology and site constraints, watch our on-demand webinar, 2019 Has Been a Good Year for ZVI Emplacement.
What is Zero Valent Iron Emplacement?
ZVI emplacement is the process of injecting the iron amendment into fractures in bedrock or soil. The in situ remediation technique is often used to treat chlorinated solvents. Initially used in trenched barrier applications nearly 30 years ago, ZVI is now also injected and blended with contaminated substances.
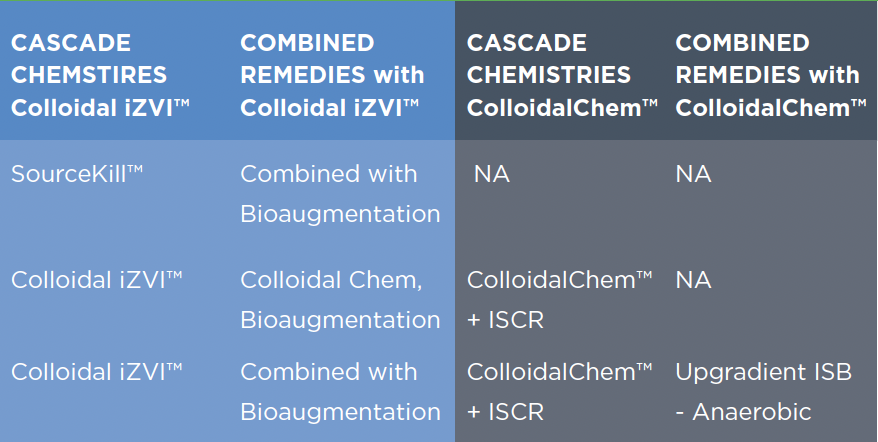
Not all ZVI are the same. They differ by size, iron content, porosity, hydraulic conductivity, surface area, reactivity, and longevity. Based on site characteristics, contaminant concentrations, and remediation objectives, ZVI can be optimized for a particular site. Often, a combined ZVI (abiotic) and carbon substrate/bioaugmentation culture (biotic) mixture is used to achieve faster remediation and limit the production of vinyl chloride breakdown products.
How Does ZVI Emplacement Work?
ZVI acts as a catalyst to encourage the breakdown of chlorinated compounds in aqueous solutions, making it excellent for remediating contaminated groundwater.
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Emplacement
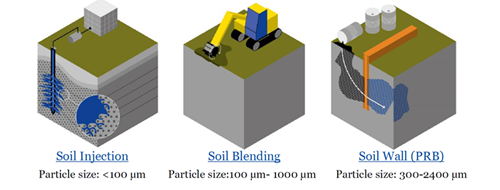
Pneumatic Emplacement: High-pressure nitrogen creates fractures, followed by hydraulic injection of ZVI amendments into the fractured zone. This is typically done using straddle packers in open boreholes, sonic casing, or direct push technology (DPT).
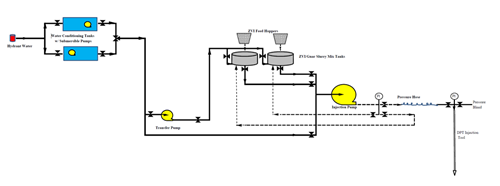
A typical process flow for hydraulic emplacement of ZVI.
ZVIs can also be emplaced using other methods, such as trenchless permeable reactive barriers (PRB), which use casing dilation. Multiple injections of ZVI—which is carried in food-grade cross-linked guar—are utilized to ensure the barrier wall is thick enough.

Trenchless Permeable Reactive Barriers (PRB)
-
PRB Method: Uses casing dilation with multiple injections of ZVI, carried in food-grade cross-linked guar, to ensure a thick barrier wall.
Soil Mixing
-
Soil Mixing Method: Performed with augers for deep applications or custom-made rotary mixers for shallow applications (generally less than 25 feet). Ideal for sites where injection approaches can't achieve necessary contact for contaminant treatment or stabilization, such as fine-grained soils and high contaminant concentrations.
Choosing the Best ZVI Emplacement Method for Your Project Site
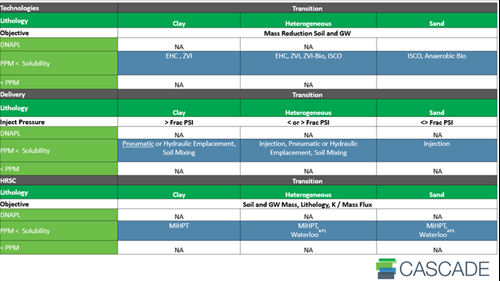
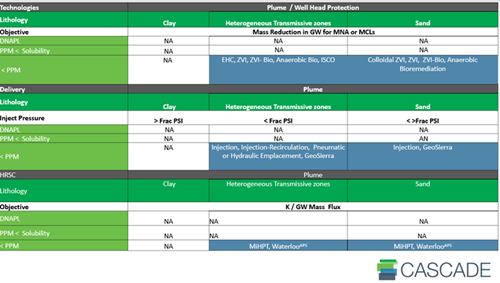
Every site is unique, and selecting the right ZVI emplacement method is crucial for achieving project goals. Consider lithology, contaminants, and whether the focus is on the source or plume zone. Below are charts to help guide your decision:
SOURCE ZONE
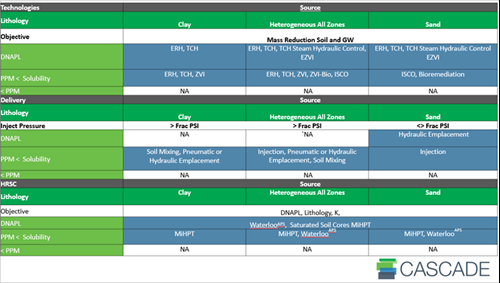
TRANSITION ZONE
PLUME ZONE
Cost-Effective Technology
ZVI is an effective and cost-efficient technology for groundwater remediation, requiring careful planning and expert application to ensure success.
ZVI Remediation Resources
-
Not All ZVI is Created Equal: How the Manufacturing Process Can Impact Project Outcomes
-
What You Need to Know About Distributing Colloidal ZVI in High K Transmissive Zones
For more information, case studies, and expert discussions, register for our on -demand webinar, 2019 Has Been a Good Year for ZVI Emplacement.
ZVI emplacement is a proven, effective in situ remediation technology. Understanding its various applications and methods can significantly impact the success of a remediation project. Ready to use ZVI for your next project? Request a quote today.